Latest edition of the Global Sustainable Investment Review confirms strong growth of ESG assets all over the world
7-minute read
In July 2021, the Global Sustainable Investment Alliance[1] (GSIA) published its fifth Global Sustainable Investment Review (GSIR) biennial report[2]. GSIA was founded back in 2010 to aggregate responsible investment market data from its members in order to analyze the global sustainable investment market and the evolution of trends in the Responsible Investment space, across the globe.
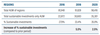
The report reveals an increase of 15% of sustainable and responsible investments (SRI) in the last two years bringing the total to USD 35.3 trillion. It represents 36% of all professionally managed assets across regions[3] covered in this report.
Figure 1. Snapshot of global assets under management, 2016-2018-2020 (USD billions)
Source: GSIR 2020
Sustainable investment assets continue to grow in most regions, with Canada experiencing the largest increase in absolute terms over the past two years (48% growth), followed by the United States (42% growth), Japan (34% growth) and "Australasia" (25% growth) from 2018 to 2020. Europe reported a 13% decline in the growth of sustainable investment assets in 2018 to 2020 due to a modified measurement methodology from which European data is drawn for this year’s report[4].
Figure 2. Snapshot of global sustainable investing assets, 2016-2018-2020 (USD billions)
Source: GSIR 2020
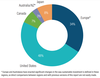
Canada is now the market with the highest proportion of sustainable investment assets at 62%, followed by Europe (42%), Australasia (38%), the United States (33%) and Japan (24%).
Figure 3. Proportion of sustainable investing assets relative to total
Source: GSIR 2020
The United States and Europe continue to represent more than 80% of global sustainable investing assets for the period 2018-2020.
Figure 4. Proportion of global sustainable investing assets by region 2020
Source: GSIR 2020
Sustainable investment strategy
Figure 4 below depicts the global growth of sustainable investing strategies from 2016-2020. The most common sustainable investment strategy is ESG integration, followed by negative screening, corporate engagement and shareholder action, norms-based screening and sustainability-themed investment. These strategies are not mutually exclusive and can be combined.
Figure 4. Global growth of sustainable investing strategies 2016-2020 (USD billions)
Source: GSIR 2020
Between 2016 and 2020:
- Sustainability themed investing registered an astonishing growth of 605%, to reach nearly USD 2 trillion assets.
- ESG Integration also shows a prominent growth of 143% from 2016, bringing the total assets managed under this strategy to approx. USD 25 trillion.
- Negative/Exclusionary screening, which topped the charts in 2018, has this year dropped to the same level as in 2016, bringing the compound annual growth to 0%.
- Norms Based Screening shows a -10% compound annual growth, due to the way it is defined and how it is applied. Some principal norms falling under this strategy are now minimum and mandatory requirements by most national governments, making it the least used by investors to classify their assets as Sustainable/ESG investments
Sustainability-themed investing, ESG integration and Corporate engagement have all experienced consistent growth during the period, whereas others like norms-based screening, positive screening as well as negative screening have experienced a more variable trajectory since 2016.
Regional Focus
GSIA report tries to explain the development of the sustainable and responsible investment market in the different region through different drivers
- policy and regulatory developments
- industry collaboration
- customer preferences and demand
- operational and market drivers.
Europe
For Europe, policy and regulatory changes and industry collaboration are the two main drivers. Some major policy changes, such as the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR), have significant impacts on the ESG/responsible investments market through new definitions set in law.
Globally, Europe accounts for 34% of the total Sustainable investing assets, valuing nearly EUR 10,.7 trillion. The European vision of Sustainable Finance which focuses on ‘double materiality’, is being seen as a necessary means for governments, markets, stakeholders, investors to be able to better understand and address the risk factoring, impact reporting and pricing negative externality, and be able to deliver the expected level of transparency. This has been mentioned as one of core recommendation by EUROSIF on the new EU sustainable finance strategy.
For this region however, Negative/Exclusionary screening remain the most used sustainable investment strategy, followed by Corporate engagement & shareholder action and ESG Integration. It is however likely that these figures hide significant differences between countries in Europe. Many European countries also seeing strong growth and investor appetite on ESG integration and Sustainability Themed Investing. Let’s keep in mind here that Europe is by far the region where Green and Sustainable Bonds markets is the most developed and where we have seen large asset managers’ long standing commitment to use ESG integration as a systematic overlay in all of their assets under management.
US and Canada
For the United States, the ‘S’ of ESG seems to outplay the other two, in terms of new policy and industry led changes. Since the election of President Biden, Socially Responsible Investing is at the center of attention in US, with over 120 investors and organizations endorsing the Investor Statement of Solidarity to Address Systemic Racism and Call to Action released by Racial Justice Investing coalition.
As of 2020, the total assets under Sustainable Investing is USD 17trn. Both Sustainability Themed Investing and ESG Integration are most used in the United States, taking USD19trn of USD 25trn and USD1.6trn of USD 2trn parts of the total.
On the other hand, Canada has emerged as the leader in 2020 when it comes to measuring the proportion of the Sustainable Investing relative to the total assets managed. Canada currently counts 61.8% of its total assets as Sustainable Investment Assets. Responsible Investment Association (RIA), has been collaborating with several other institutions and organizations to come up with initiatives to promote the transition to a low carbon economy. However, Canada accounted for 7% of the total Sustainable Investing Assets, 3,1 trillion Canadian Dollar in value.
Japan
In Japan, a move of investments towards cleaner assets is noted, mainly through ESG integration and Thematic Investing, good practice examples and effective participation by life insurers in addressing climate change.
The Japan Sustainable Investment Forum (JSIF) is collaborating with more and more institutional investors locally to integrate sustainable investing practices into their investment portfolios and financial decisions. Corporate engagement and Shareholder Action is the most preferred strategy. The country also ranks third when it comes to growth in Sustainable Investing assets in 2020 compare to 2018 level, with 34%, representing JPY ¥310,039 bn (USD 2.8 billion) as of 2020 report. This makes 8% of the global share of Sustainable Investing assets for Japan, just ahead of Canada.
Australia and New Zealand
A combination of regulatory drivers and industry drivers are responsible for the growth of Sustainable Investment market in Australia and New Zealand. Changes in the policy of the Australian financial system to align it with a more climate change resilient and prosperous future has prompted many investors across the region to engage actively, along with adapting strategies to transition to a low carbon economy. In New Zealand, an important legislative development is The Climate Change Response (Zero Carbon) Amendment Act 2019[5], which provides a framework for New Zealand to develop and implement Paris Agreement aligned climate change policies. A 25% growth in Sustainable Investing assets was measured from 2018 levels. In terms of value, AUD 1,295 bn which makes 3% of the total Sustainable Investing assets, puts Australasia region at the bottom most position out of the 5 assessed regions.
Africa
As compared to the 2018 report, this one shows substantial growth and development of Responsible Investment market in Nigeria and Kenya, along with South Africa being the financial hub of the region. Policy and regulatory changes were instrumental drivers for such growth in these countries. Moreover, constant efforts to develop the carbon markets in parts of East and West Africa can be seen, as market actors have formed alliances to develop emissions trading markets. Positive developments in the Green Bond markets of this region is also driving the increase in Sustainable investments, with growing demands from retail side.
Conclusion
While there is clearly a long way to go, the progress made globally with respect to investor’s appetite for sustainable investment products is compelling. ESG assets surpassed USD 35 trillion, up from USD 30.6 trillion in 2018 and USD 22.8 trillion in 2016 – to become a third of the total global assets under management, according to this report.
The GSIA assumes that with 15% growth, corresponding to half of the pace of the past five years, ESG assets could exceed USD 50 trillion by 2025.
Even though, this GSIA report does no breakdown the asset class or investors’ type when talking of Sustainable Investing Assets which can lead to some unclarity, this is the only report which gives such a macro-level view of the market trends.
The USD 3 trillion ESG debt market could also grow to USD 11 trillion by 2025, assuming it expands at half the pace of the past five years. Organic growth will not likely slow as it will be led by companies, development projects and central banks, along with pandemic and green-recovery efforts, and the push to Net Zero.
EU pledges of 100 billion euros to support employment and 225 billion euros to fund a post-pandemic recovery, U.S. President Joe Biden's USD 1.2 trillion infrastructure plan and the challenge of China's 2023 green-debt maturities signal ample room for new debt issuance.
Sustainability-linked bonds and loans are emerging as a new asset class and may help the next wave of growth by opening the tap to a broader set of industries and objectives.
Looking ahead, we can say that with the policy support such as that being displayed by the governments around the world, and commitments like various Net Zero Investors Alliances, and many others, including those from China and APAC region, are likely to feed a double digit compound annual growth of responsible investment markets in the coming years, as shown by the GSIR over the last decade.
[1] The GSIA is a network of regional sustainable investment forums composed of EUROSIF (European Sustainable Investment Forum) in Europe, USSIF (Forum for Sustainable and Responsible Investment in US) and RIA (Responsible Investment Association in Canada) in America , RIIA (Responsible Investment Association Australasia) and JSIF (Japan Sustainable Investment Forum) in Asia Pacific among other forums of other regions.
[2] GSIA 2020 Review available here
[3] The report covers the global trend of 5 main regions: Europe, United States, Canada, Australia and New Zealand and Japan. Additionally, this report also tracks the trend for the United Kingdom, China, and across Latin America, Africa and Asia, to form a global picture of the sustainable investment industry.
[4] This reflects a period of transition associated with revised definitions of sustainable investment that have become embedded into legislation in the European Union as part of the European Sustainable Finance Action Plan.
[5] See here.
To go further:
- Climate Bond Initiative, "Record $700bn of Green, Social & Sustainability (GSS) Issuance in 2020: Global State of the Market Report" (Avril 2021) - available here.
- Eurosif, "Letter to the Commission – on the new EU Sustainable Finance Strategy" (June 2021) - available here.
- GSIA, Global Sustainable Investment Review 2020 - available here.
- EFAMA, Market Insights (November 2020) - available here.